Bittensor Halving: What the TAO Supply Cut Means for AI and Crypto
Bittensor halving explained with TAO supply changes, market impact, and why this AI driven network may see rising demand.

The first ever Bittensor halving is one of the most anticipated events in the AI crypto sector. As the TAO emission rate falls by fifty percent, developers, miners, and investors are trying to understand how this new supply shock could reshape the network. Bittensor has already emerged as one of the most active decentralised AI ecosystems, and its halving could become a defining moment for the protocol.
Table of Content
- What is Bittensor?
- What is Bittensor halving?
- How the Bittensor Halving Works
- Halving Impacts TAO Emissions
- Key Benefits and Use Cases of the Bittensor Halving
- Common Questions
- At glance
- About Onfinality
What is Bittensor?
Bittensor is a decentralised AI network that rewards machine learning models for providing high quality inference. Instead of centralised ownership, it uses a peer to peer marketplace where AI models compete across specialised subnets. Participants earn TAO tokens based on the performance and usefulness of their contributions.
Key features of Bittensor
- Open source AI network powered by miners running ML models
- Reward distribution based on actual performance signals
- Multiple subnets designed for different AI tasks
- Token incentives that encourage better and more efficient models
It blends blockchain tokenomics with machine learning, creating a collaborative AI economy.
What is Bittensor halving?
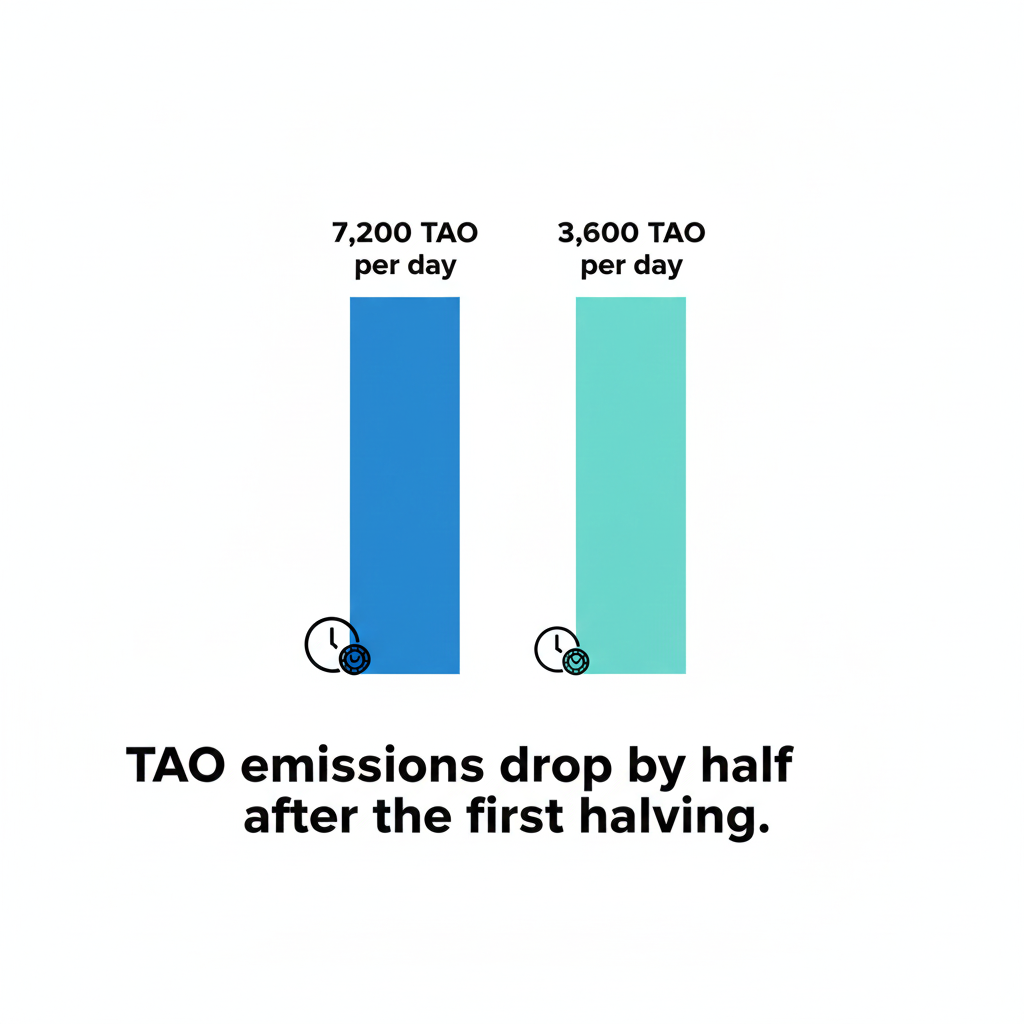
Bittensor supply is capped at 21 million similar to BTC and it follows the same halving concept. The Bittensor halving is a scheduled reduction in TAO block rewards where emissions drop by fifty percent, i.e, 7200 TAO/block reduces to 3600 TAO/block. This mirrors the halving concept known from Bitcoin, where new token issuance decreases over time to improve economic sustainability. Current halving is scheduled on 14th December.
How the Bittensor Halving Works
- Bittensor produces a new block roughly every 12 seconds.
- Each block issues 1 TAO that is shared among miners, validators, subnet owners, and delegators.
- This leads to about 7,200 TAO entering circulation each day.
- After the first halving, daily emissions will fall to about 3,600 TAO.
- Bitcoin follows a block count schedule for halvings, but Bittensor triggers its halving once the total circulating supply reaches a defined level.
Halving Impacts TAO Emissions
The halving fundamentally transforms the long term emission landscape of Bittensor. With each supply checkpoint, fewer TAO tokens enter circulation, which reshapes incentive structures across the entire AI network.
Key emission impacts
- Slower inflation improves token stability
- Greater scarcity increases the strategic value of TAO
- More efficient subnets as miners compete for limited rewards
- A long tail reward curve ensures sustainability as emissions approach near zero
This staged tapering means the network gradually shifts from growth incentives to efficiency incentives, aligning long term value with model performance rather than inflation.
Key Benefits and Use Cases of the Bittensor Halving
Potential Benefits
- Scarcity driven value dynamics as new TAO supply decreases
- Higher quality AI models due to competitive mining pressure
- Greater sustainability of long term emissions
- More market awareness of decentralised AI networks
Use Cases Strengthened by the Halving
- AI inference networks requiring scalable compute
- Decentralised model marketplaces where performance earns rewards
- Autonomous agents that rely on distributed intelligence
- Data intensive machine learning systems
Common Questions
Does the TAO price rise after the halving
Supply tightening can influence price discovery, but no outcome is guaranteed. Price movement depends on network demand, miner behaviour, and broader market conditions.
Will Bittensor halving affect the user
Bittensor halving will not the affect the user's operation
How often does the Bittensor halving occur
The halving follows a fixed emission schedule written into the protocol. Frequency and exact parameters can be verified on the official network data dashboards such as TaoStats.
What happens to miners after the halving
Rewards are reduced, but competitive miners may continue to earn significant TAO based on their subnet ranking and model performance. The halving encourages innovation and efficiency.
At glance
The first Bittensor halving represents a major economic and technical milestone for the TAO ecosystem. Reduced emissions, growing demand for decentralised AI, and a performance based incentive model create strong conditions for network growth.
Key takeaways
- TAO supply will tighten significantly
- Miner competition may increase
- Network sustainability improves
- AI demand growth can amplify halving effects
This event positions Bittensor as a unique contender in the decentralised AI landscape.
About Onfinality
OnFinality is a blockchain infrastructure platform that serves hundreds of billions of API requests monthly across more than 130 networks, including Avalanche, BNB Chain, Cosmos, Polkadot, Ethereum, and Polygon. It provides scalable APIs, RPC endpoints, node hosting, and indexing tools to help developers launch and grow blockchain networks efficiently. OnFinality’s mission is to make Web3 infrastructure effortless so developers can focus on building the future of decentralised applications.
